WISDOM TEETH SURGERY
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last teeth to erupt in your mouth. This generally occurs between the ages of 17 and 25, a time of life that has been called the “Age of Wisdom.”
Anthropologists note that the rough diet of early humans resulted in the excessive wear of their teeth. Normal drifting of the teeth to compensate for this wear ensured that space was available for most wisdom teeth to erupt by adolescence. The modern diet, which is much softer, and the popularity of orthodontic tooth straightening procedures produce a fuller dental arch, which quite commonly doesn’t leave room for the wisdom teeth to erupt, thereby setting the stage for problems when the final four molars enter the mouth.
What is an Impacted Tooth?
A tooth becomes impacted when there is a lack of space in the dental arch and its growth and eruption are prevented by overlying gum, bone or another tooth. Impacted and partially impacted teeth can be painful and lead to infection. They may also crowd or damage adjacent teeth or roots.
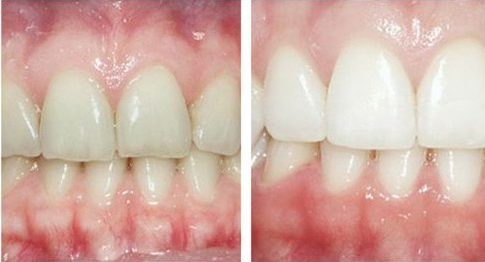
Food particles and germs get trapped around the edge of the wisdom teeth resulting in plaque that further results in decayed teeth and break away the teeth and can lead to:
- Tooth decay (dental caries): When the decay gets more then it results in cavities in the teeth that affect the overall oral health.
- Periodontal disease: Periodontal or gum disease occurs when the toxins are released from the plaque that irritates your gums and leave them painful and swollen. They also affect the surrounding teeth and area around the wisdom teeth.
- Gum disease: Gum disease can also affect the surrounding teeth and the bone around the wisdom teeth.
- Pericoronitis: When plaque causes an infection of the soft tissue that surrounds the tooth.
- Cellulitis: It is a bacterial infection in the cheek, tongue or throat.
- Abscess: This problem occurs when pus collects in your wisdom teeth or the surrounding tissue due to a bacterial infection.
- Cysts and benign growths: This is a very rare case in which a wisdom tooth that hasn’t cut through the gum develops into a cyst.
